![]()
In today’s post we will talk about network scanning using Nmap using our Android device. Nmap is one of the most popular utility for network exploration. It supports ping scanning (determine which hosts are up), many port scanning techniques, version detection (determine service protocols and application versions listening behind ports), and TCP/IP fingerprinting (remote host OS or device identification) and many more. Besides explaining NetHunter’s Nmap user interface and its usage, we will take one extra step further to actually demonstrate its functionality on our router to search for open ports and known vulnerabilities as well as how to access files on smartphone through open ports of file manager apps.
Nmap Scan
Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is a widely used and highly versatile network scanning tool. It is available as part of the NetHunter system with graphical user interface (GUI) that triggers its command line version and is used for network exploration. Simple Nmap Scan interface you can see in Figure 1.

Using Nmap you can discover hosts on the network, port scan, enumerate services running on the network, detect OS and scan against known vulnerabilities known as Nmap Script Engine (NSE). It allows us to explore various scanning techniques including TCP SYN, UDP, ICMP and other scans. All you need to do is enter in edit box is IP address, hostnames, networks etc. When you launch the scan, NetHunter Terminal will start command line version of Nmap and scan your input address.
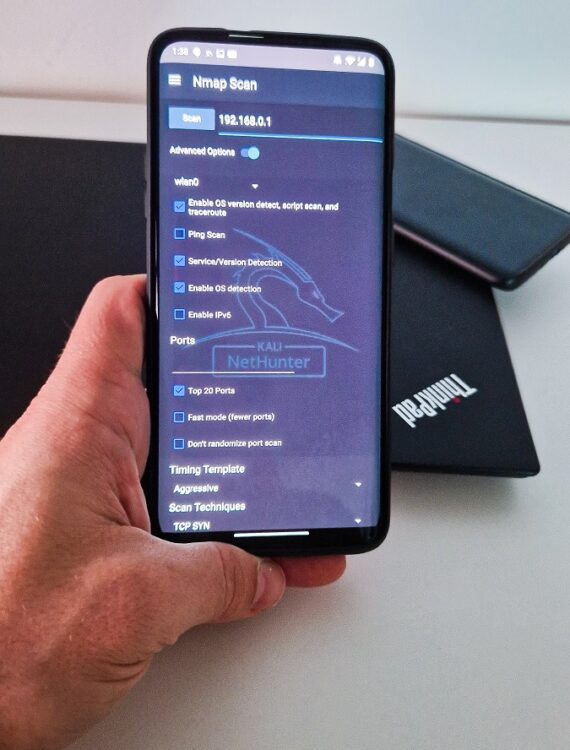
Advanced option
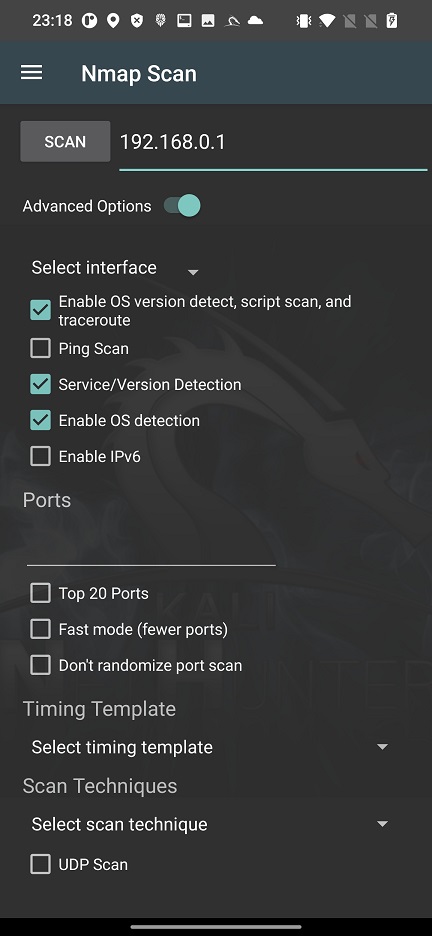
To launch in-depth scan on targets without typing a long string in command line, you can use Nmap with Advanced Options, see Figure 2.
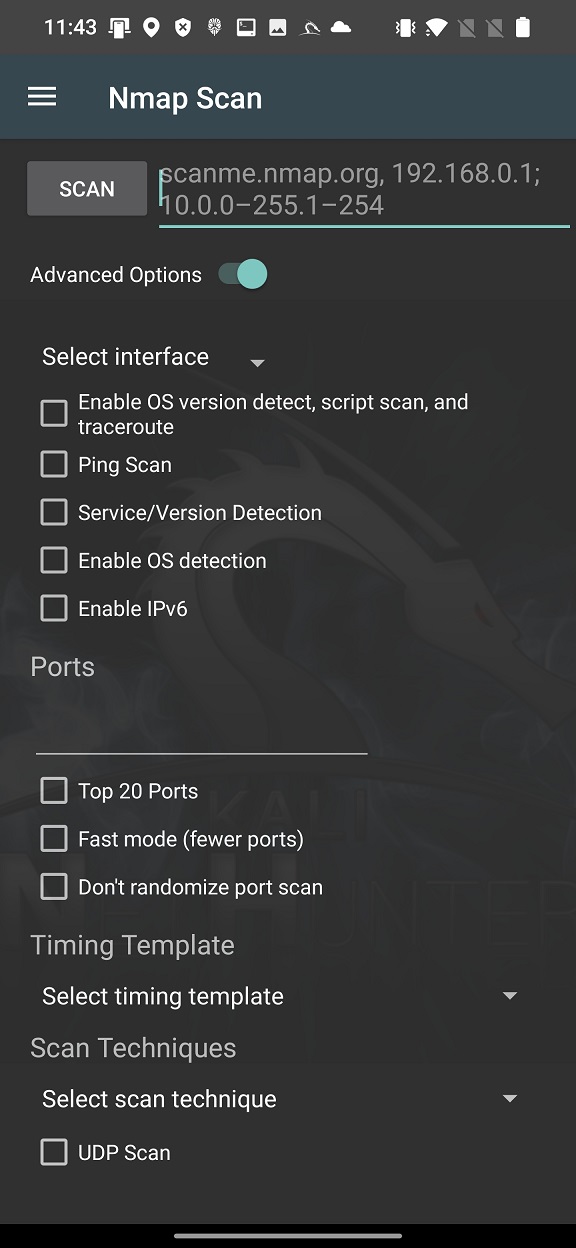
These options cover only the most used Nmap arguments, not all of them. In your scan you can conveniently enable particular interface such as wlan0, wlan1, eth0 or rndis0, OS and service detection, top 20 or custom port scan, select timing template and choose scan technique.
Based on the Nmap Scan source code available on GitLab, for better understanding of these options, I assigned actual argument to each of the option In Figure 3.
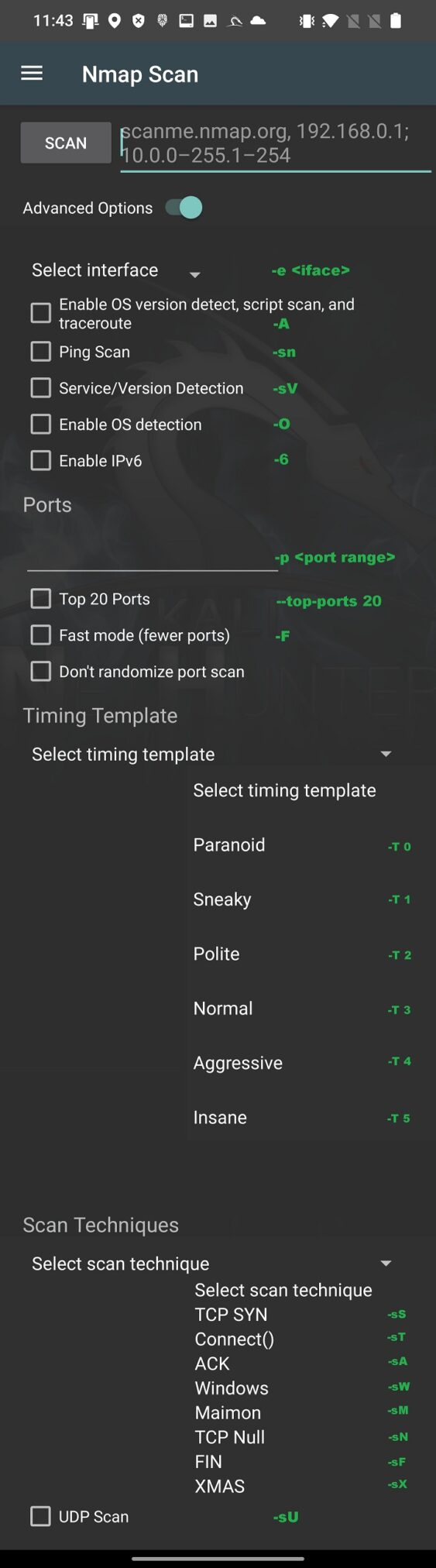
If you want to perform more in-depth and specific scan, they I advise you to use Nmap within NetHunter Terminal app.
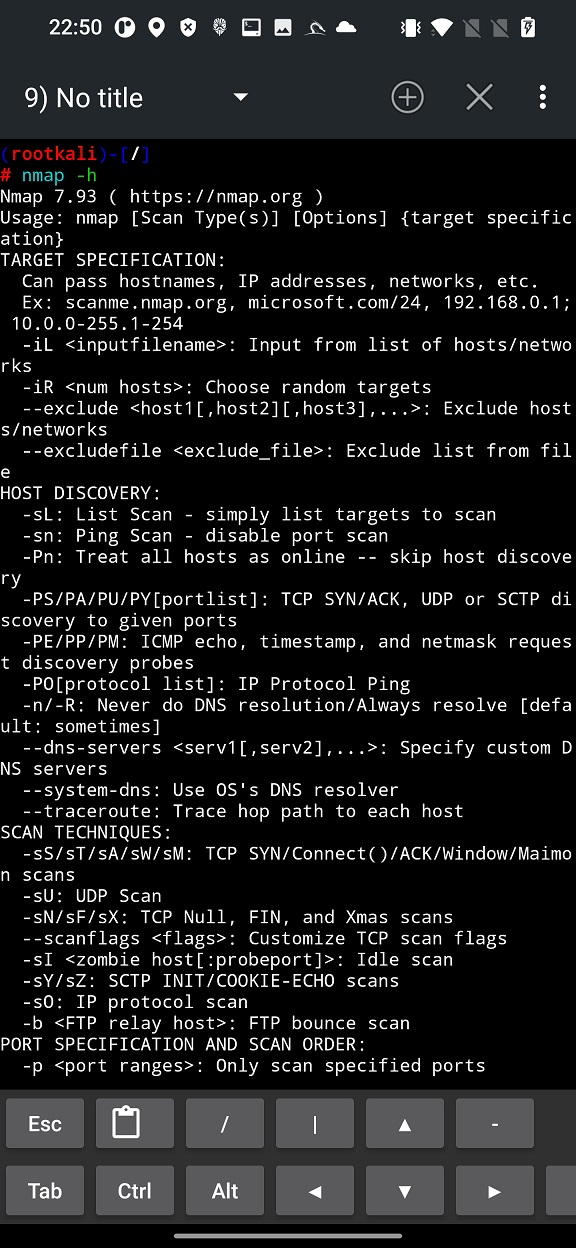
As a result, these scans can help ethical mobile hacker to understand potential entry points for network attacks or in assessing the security posture of a network.
Nmap router
In this example we try to scan and obtain details about our local Wi-Fi router. Our NetHunter smartphone is already connected to Wi-Fi network that is under our control. From Network details of currently connected networks, we can obtain IP address of our router (Gateway).
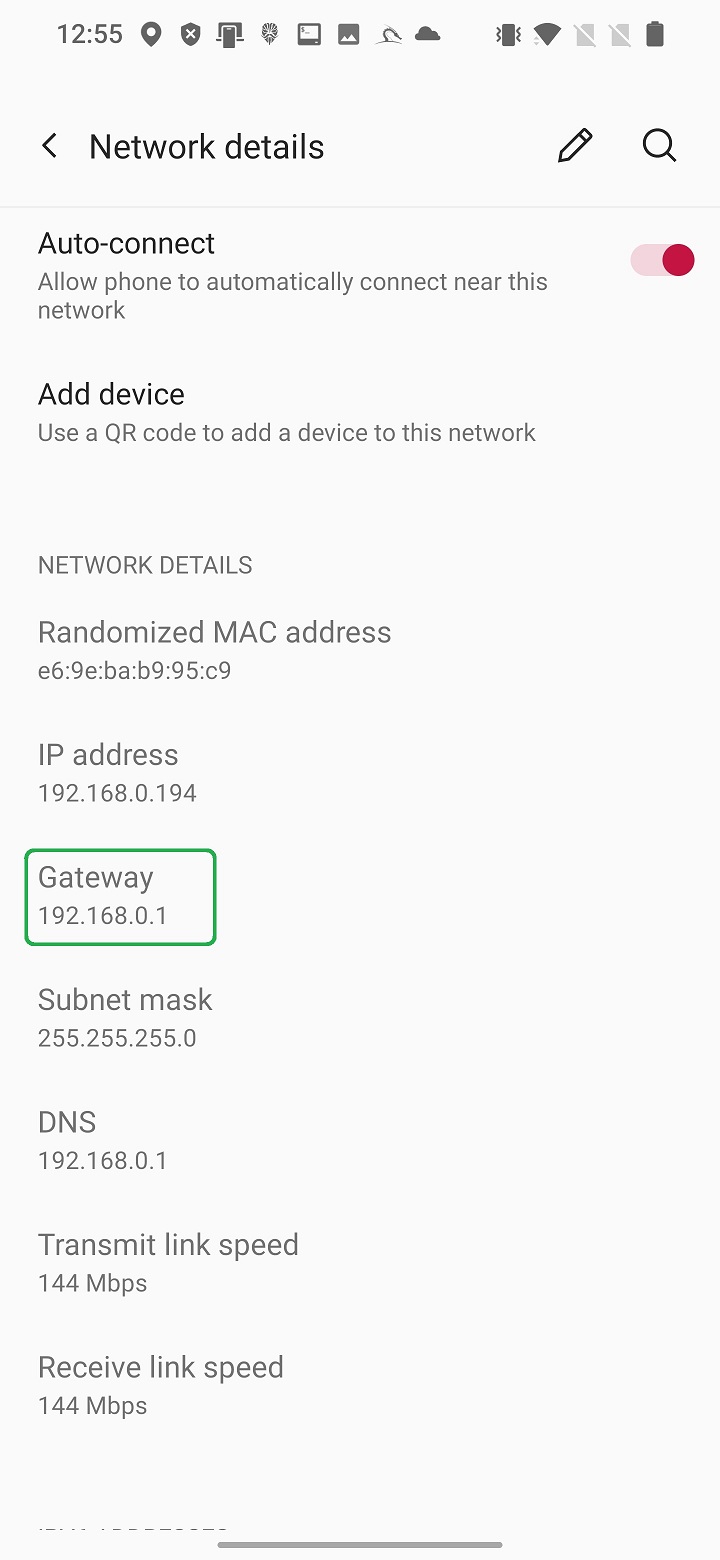
This IP address we will use as a target to perform simple Nmap scan. Enter the IP in edit box and hit SCAN button as visible in Figure 6.

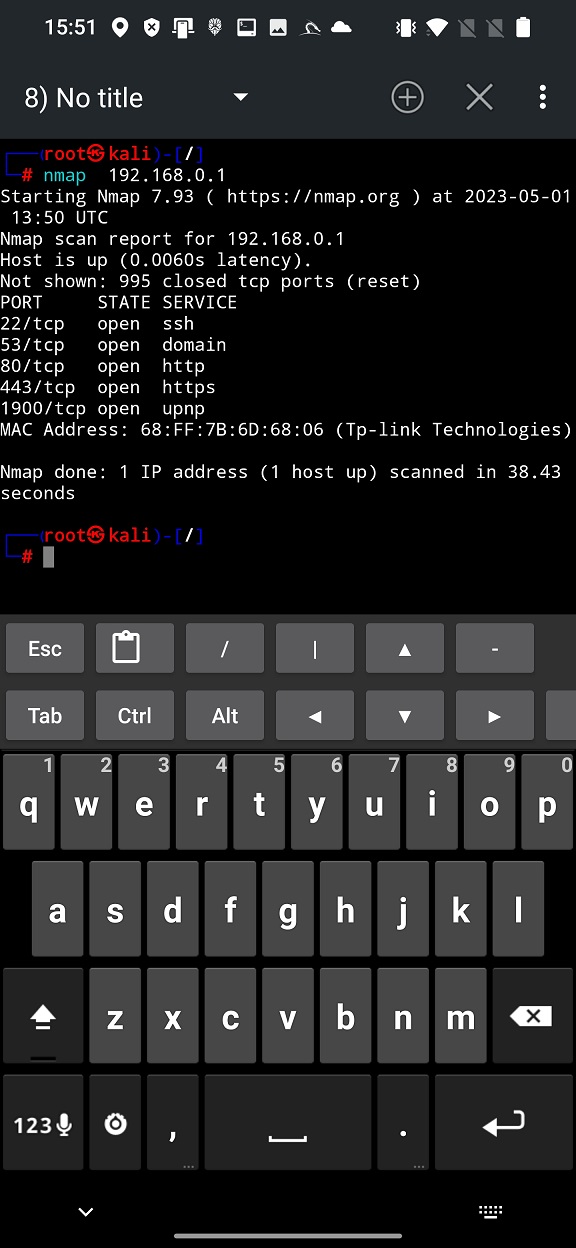
Simple graphical interface launches Nmap in NetHunter terminal with provided arguments – only IP address. From the plain scan result displayed in Figure 4., we can tell there are opened five ports (22, 53, 80, 443, 1900) running five services (ssh, domain, https, https and upnp), MAC address and brand of our router (Tp-link). This gives us brief information about our access point.
To perform quick more in-depth scan, we enable Advanced Options and select more options to fingerprint our device as selected in Figure 8.
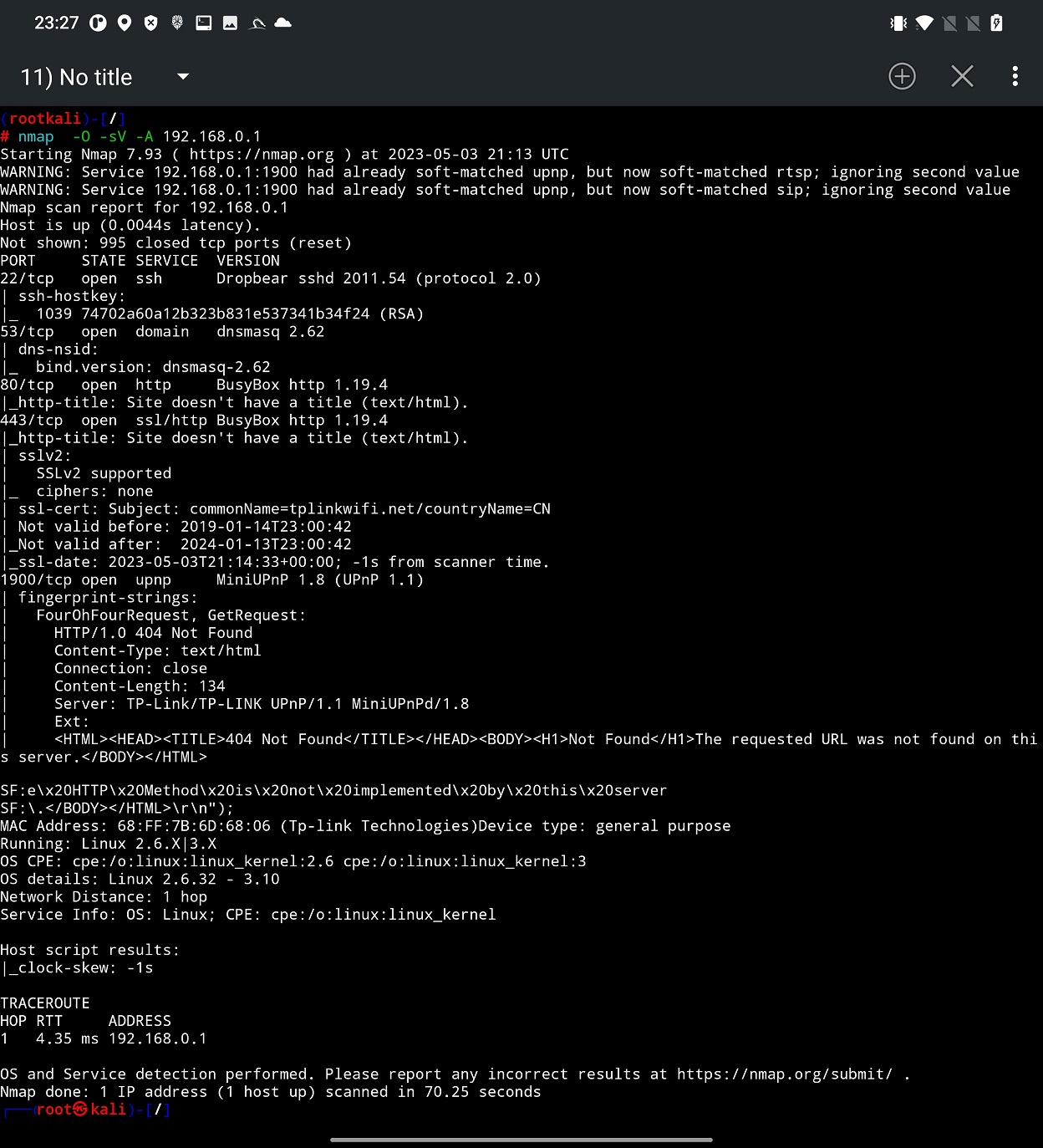
From the output, see Figure 9, we identified Linux version running on our tested router, open ports with version of services are there running. To scan all port and their services you can select custom range of ports in edit box such as 0-65535.
Based on the fingerprinted OS and version of running services of various open ports we can perform vulnerability scan. Unfortunately, it is not part of Nmap Scan user interface, so we have to use Terminal. Nmap provides script scan option, where you have to provide a path to particular script or just enter script category. In our scan we will go with scan category. Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) defines for us list of 14 categories that are auth, broadcast, brute, default. discovery, dos, exploit, external, fuzzer, intrusive, malware, safe, version, and vuln. Explanation to each of them you can find on official Nmap website. We will use vuln category, that focuses on identifying vulnerabilities present in the target system. These scripts leverage various techniques to detect common security issues, known vulnerabilities, default or weak configurations, and potential entry points for exploitation. To launch this scan, you have to include -sV and –script vuln arguments, see Figure 10.
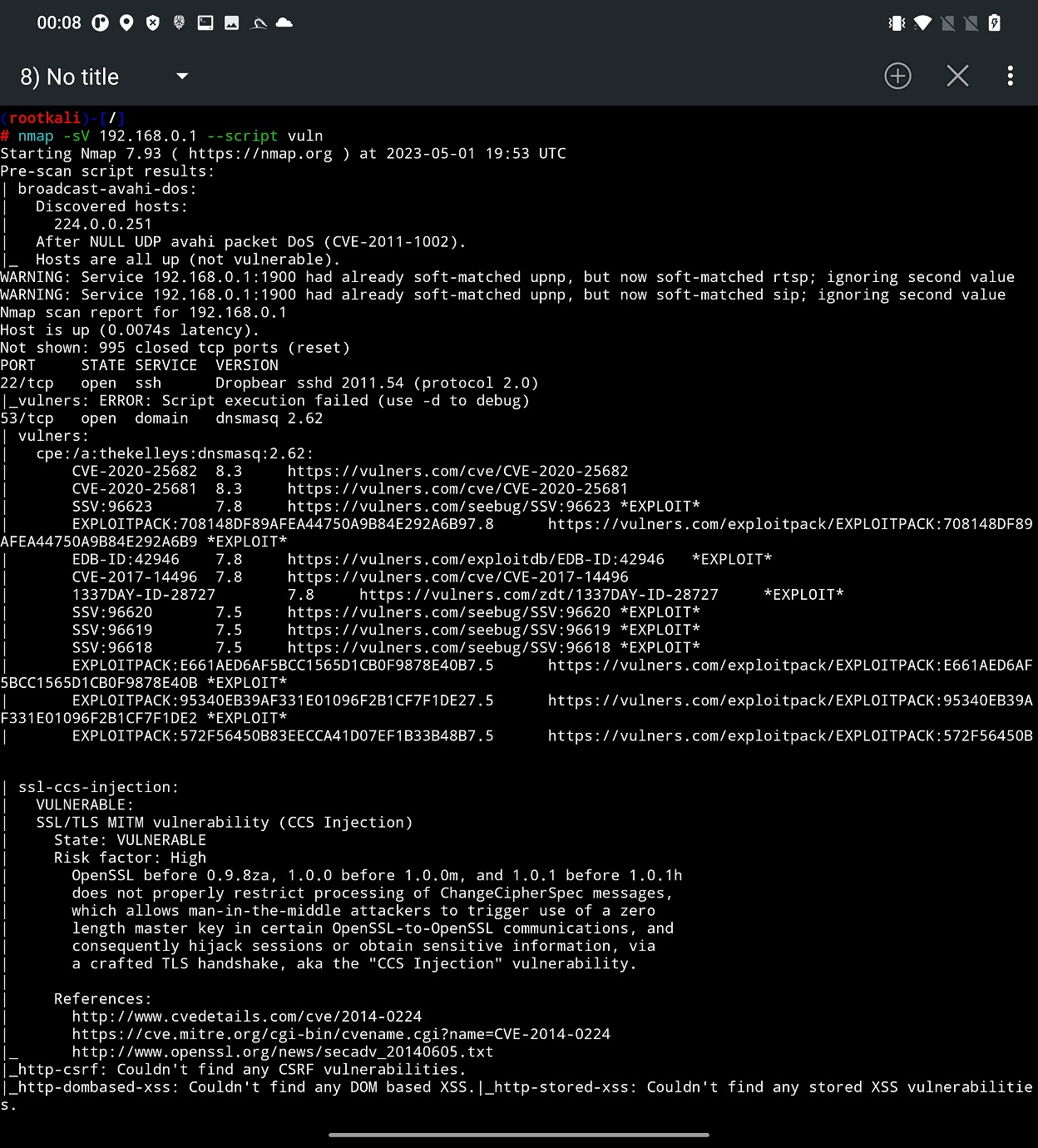
From the scan result you can identify potential issues on targeted device that are tracked by CVE. Based on them, you can use SearchSploit to look for further details or even an exploit. In some cases, such exploit could be even included in Metasploit, which means that with no extra effort you can verify if you can exploit them.
Scan file manager apps
Most of a file manager apps allow user to create local server that is accessible from other devices, such as a computer, for files, photos, music sharing. This option needs to be manually enabled by a user. However, problem might be when user forgets about it, and the app keeps the port open leaving the access to external storage (/storage/0/emulated/) to anyone on the network. If this happens on your home network, you might not consider it as a problem. However, if you leave your home network and connect to public Wi-Fi with this option still enabled, your device data might be at risk.
In the video below I created a quick demonstration.
Some of these apps prevent access to unauthorized users by requesting user name and password. This security feature for File Commander app with over 100,000,000 installs on Google Play was missing.
Prevention tips
While Nmap is a useful and legitimate tool for network administrators and security professionals, it can also be used by malicious actors to scan and attack your network. Therefore, it is important to take some preventive measures to protect your network from Nmap attacks. Some of the tips you can follow are:
- Prevention: Make sure your network requests user authorization using a strong password to restrict unwanted hackers to scan devices on your network.
- Firewall: Use a firewall to block or limit incoming and outgoing traffic on your network. You can configure your firewall to allow only trusted hosts and services, and deny or drop any suspicious or unwanted packets. You can also use firewall rules to detect and block common Nmap scan types, such as SYN, ACK, FIN, XMAS, NULL, or UDP scans.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable any unnecessary or unused services and ports on your network devices and systems. By reducing the exposed attack surface, you limit the potential impact of Nmap scans.
- Network Segmentation: Segment your network into smaller, isolated subnetworks. This helps limit the impact of Nmap attacks by isolating critical systems and reducing the attack surface.
- Monitoring: Use network monitoring and intrusion detection systems to detect and respond to any Nmap scans or attacks on your network. You can use tools such as Snort, Suricata, Bro, or Wireshark to analyze your network traffic and identify any anomalies or signatures of Nmap scans.
- Update: Keep your systems and devices updated and patched with the latest security updates and fixes. You can also use tools such as Nmap itself, Nessus, or OpenVAS to scan your own network and find any vulnerabilities or misconfigurations that need to be fixed.
Conclusion
Nmap is a great tool for network scanning and security testing, and it works perfectly even on NetHunter. With NetHunter, you can use Nmap on your mobile device, and take advantage of its portability, flexibility, and convenience. You can scan any network you are connected to, and use the results to find vulnerabilities, exploits, or other information. You can also customize your scans with various options and parameters, and save or export your results for further analysis. Nmap on NetHunter is a must-have tool for any cybersecurity enthusiast or professional who wants to have a powerful and portable hacking device in their pocket.


How i download in Android
Nice tutorial on using Nmap for network scanning! I’ve been looking for a comprehensive guide on this topic, and your post has covered all the basics. Thanks for sharing your knowledge!